- שפות תיכנות

- בניית אתרים

- אבטחת מידע ו-IT

- Web Securityאנונימיות, פרטיות וחוק ברשת האינטרנטקריפטוגרפיההנדסה לאחור (reversing)אבטחת ססמאותאבטחת מידע - כלליטרוינים ווירוסיםאבטחת Windows
- מגזין Digital Whisper:Digital Whisper - גליונות מלאיםDigital Whisper - הגליון הראשוןDigital Whisper - הגליון השניDigital Whisper - הגליון השלישיDigital Whisper - הגליון הרביעיDigital Whisper - הגליון החמישיDigital Whisper - הגליון השישיDigital Whisper - הגליון השביעיDigital Whisper - הגליון השמיניDigital Whisper - הגליון התשיעיDigital Whisper - הגליון העשיריDigital Whisper - הגיליון האחד עשרDigital Whisper - הגיליון השנים עשרDigital Whisper - הגיליון השלושה עשרDigital Whisper - הגיליון הארבעה עשרDigital Whisper - הגיליון החמישה עשרDigital Whisper - הגיליון השישה עשרDigital Whisper - הגיליון השבעה עשרDigital Whisper - הגיליון השמונה עשרDigital Whisper - הגיליון התשעה עשרDigital Whisper - הגיליון העשריםDigital Whisper - הגיליון העשרים ואחדDigital Whisper - הגיליון העשרים ושנייםDigital Whisper - הגיליון העשרים ושלושהDigital Whisper - הגיליון העשרים וארבעהDigital Whisper - הגיליון העשרים וחמישהDigital Whisper - הגיליון העשרים ושישהDigital Whisper - הגיליון העשרים ושבעהDigital Whisper - הגיליון העשרים ושמונהDigital Whisper - הגיליון העשרים ותשעהDigital Whisper - הגיליון השלושיםDigital Whisper - הגיליון השלושים ואחדDigital Whisper - הגיליון השלושים ושנייםDigital Whisper - הגיליון השלושים ושלושהDigital Whisper - הגיליון השלושים וארבעה
- מדעי המחשב

- מתמטיקה

- פיסיקה

יש לראות בכל האמור באתר underwar.co.il מידע כללי בלבד. כל פעולה שנעשית על פי המידע והפרטים האמורים באתר underwar.co.il הינה על אחריות הגולש בלבד. בשום מקרה אתר underwar.co.il ו/או ניר אדר ו/או צוות מנהלי פורום underwar.co.il ו/או שאר חברי הפורום אינם אחראיים בשום צורה ואופן לתוצאות השימוש במידע המובא באתר זה. עשיית שימוש במידע המובא באתר underwar.co.il, הינה על אחריותו של הגולש בלבד.
פרוייקט UnderWarrior - מדריכים, מאמרים, סיכומים וחומרי לימוד בתחומי תכנות, מתמטיקה, אבטחת מידע ועוד
1997-2025 © כל הזכויות שמורות לניר אדר
1997-2025 © כל הזכויות שמורות לניר אדר

![plot:\[{L_1},{L_2}\]](/documentResources/261/plot_253.png) שפות כלשהן כך שמתקיים
שפות כלשהן כך שמתקיים ![plot:\[{L_1} \leqslant {L_2}\]](/documentResources/261/plot_254.png) , אזי:
, אזי:![plot:\[{L_1} \in R \Leftarrow
{L_2} \in R\]](/documentResources/261/plot_255.png) (באופן שקול: אם
(באופן שקול: אם ![plot:\[{L_2} \notin {\text{R}}
\Leftarrow {L_1} \notin {\text{R}}\]](/documentResources/261/plot_256.png) )
)![plot:\[{L_1} \in RE \Leftarrow
{L_2} \in RE\]](/documentResources/261/plot_257.png) (באופן שקול: אם
(באופן שקול: אם ![plot:\[{L_2} \notin {\text{RE}}
\Leftarrow {L_1} \notin {\text{RE}}\]](/documentResources/261/plot_258.png) )
)![plot:\[{L_1} \in {\text{CO -
RE}} \Leftarrow {L_2} \in {\text{CO - RE}}\]](/documentResources/261/plot_259.png) (באופן שקול: אם
(באופן שקול: אם ![plot:\[{L_2} \notin {\text{CO -
RE}} \Leftarrow {L_1} \notin {\text{CO - RE}}\]](/documentResources/261/plot_260.png) ).
).![plot:\[{\text{R}},{\text{RE}},{\text{CO - RE}}\]](/documentResources/261/plot_261.png) .
.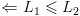 קיימת פונקציה
קיימת פונקציה  המהווה רדוקציה מ-
המהווה רדוקציה מ- ל-
ל-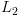 ובפרט קיימת מ"ט
ובפרט קיימת מ"ט 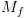 המחשבת אותה (ניתנת לחישוב). בנוסף מכיוון ש-
המחשבת אותה (ניתנת לחישוב). בנוסף מכיוון ש-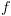 מלאה,
מלאה, 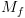 עוצרת תמיד.
עוצרת תמיד.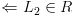 קיימת
קיימת 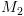 שעוצרת תמיד ו-
שעוצרת תמיד ו-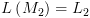 . נבנה מ"ט
. נבנה מ"ט 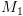 עבור
עבור 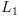 על קלט
על קלט 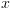 :
: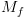 על מנת לחשב את
על מנת לחשב את 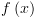 .
.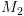 על
על 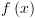 .
אם
.
אם 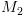 מקבלת/דוחה,
מקבלת/דוחה, 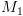 עושה כמוה.
עושה כמוה.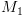 עוצרת תמיד (כי
עוצרת תמיד (כי 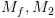 עוצרות תמיד).
עוצרות תמיד).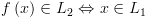 (עקב תקפות
(עקב תקפות 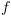 ) ומכאן מנכונות
) ומכאן מנכונות 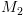 נובע כי גם
נובע כי גם 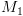 עוצרת
ומקבלת על
עוצרת
ומקבלת על 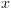 .
.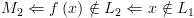 דוחה את
דוחה את 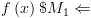 דוחה את
דוחה את 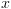 .
.
החלק הראשון
בבקשה